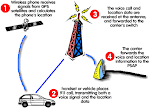
IEEE GPS PROJECTS
GPS BASED IEEE PROJECTS
1.Efficient Cost-Based Tracking of Scheduled Vehicle Journeys
YEAR OF PUBLISHING : 2008
Applications in areas such as logistics, cargo delivery, and collective transport involve the management of fleets of vehicles that are expected to travel along known routes according to schedules. There is a fundamental need by the infrastructure surrounding the vehicles to know the actual status of the vehicles. Since the vehicles deviate from their schedules due to road construction, accidents, and other unexpected conditions, it is necessary for the vehicles to communicate with the infrastructure. Frequent updates introduce high communication costs, and server-side updates easily become a bottleneck. This paper presents techniques that enable the tracking of vehicle positions and arrival times at scheduled stops with little communication, while still offering the desired accuracy to the infrastructure of the status of the vehicles. Experimental results with real GPS data from buses show that the proposed techniques are capable of reducing the number of updates significantly compared to a state-of-the art approach where vehicles issue updates at pre-defined positions along their routes. 2008
2. Software/hardware co-design of a vehicle trajectory monitoring system
YEAR OF PUBLISHING : 2008
Using a GPS to navigate, a guard locates a car theft and utilizes vehicle tracking that is, at present, widely employed. In this paper the terminal device using a microcontroller combines a GPS and a GSM/GPRS to make a portable and remote controlling device, and an embedded server is used as a transfer location server. In this way one accomplishes real-time vehicle trajectory monitoring. Clients can remotely monitor a vehiclepsilas position anywhere. Besides, as we have designed the remote monitoring using a virtual comport to combine the existing commercial or free electronic map directly, we need not develop or revise the electronic map software. 2008
3. Intelligent Fleet Management System with Concurrent GPS & GSM
YEAR OF PUBLISHING : 2008
Real-Time Positioning Technology Fleet management system is a rapid growing industry. This system helps institutions to manage vehicle fleet efficiently and effectively through smart allocation of resources. In this project, an intelligent fleet management system which incorporates the power of concurrent Global Positioning System (GPS) and Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) real-time positioning, front-end intelligent and web-based management software is proposed. In contrast to systems which depend solely on GPS positioning, the proposed system provides higher positioning accuracy and is capable to track the target at areas where GPS signals are weak or unavailable. The terminal is powered by Front-End Intelligent Technology (FEI), a comprehensive embedded technology that is equipped with necessary artificial intelligence to mimic human intelligence in decision-making for quicker response, better accuracy and less dependence on a backend server. With less dependency on the backend, large scale fleet management system can be implemented more effectively. The proposed system is successfully implemented and evaluated on twenty vehicles including buses and cars in Universiti Teknologi Malaysia (UTM). Results from the test-bed shown that user can monitor and track the real-time physical location and conditions of their vehicles via Internet or Short Message Service (SMS). The web-based fleet management software also helped the user to manage fleets more effectively. 2008
4. The Design of Vehicle emergent calling system based on gprs
YEAR OF PUBLISHING : 2008
Combining with the working principle of Intelligent Transport System, and with the purpose of enhancing the security of modern traffic, this paper brings forward a project of building a kind of automobile emergent calling system which starts-up with the starting of airbag, the wireless date transport modem, which is droved by serial interface, transmitted the acquired data to the remote monitoring center. The design of the hardware circuit implement, the design of software and the design of building monitor and control center are demonstrated. And finally, the key technique of the system is also discussed. 2008
5. GPS Based Mobile Tele Monitoring and Management System for Inter cities Public Transportations
YEAR OF PUBLISHING : 2008
This paper presents a Tele-monitoring and management system for inter-cities transportation vehicles such as taxis and buses. The system is based on a stand-alone single-board embedded system that is equipped with GPS and GSM modems that is installed in the vehicle. A personal computer based GSM-Server is installed at transportation's head-quarter. While the vehicle is on the move, its real-time parameters such as speed, location, estimated arrival time, road condition and surrounding weather status are reported as SMS message to the transportation's head-quarter GSM-Server for further process. A software package is developed and installed in GSM-server to read, process, analyze and store the incoming SMS messages. Graphical User Interface (GUI) and software management package are developed using Active Server Pages (ASP) and HTML to monitor the fleet and to build profile for each vehicle and driver. The system utilizes the readily available GSM mobile public networks; therefore the fleet administration should not worry about upgrading or maintaining such network. 2008
6.Development of pedestrian-to-vehicle communication system prototype for pedestrian safety using both wide-area and direct communication
YEAR OF PUBLISHING : 2008
We propose a prototype pedestrian-to-vehicle communication system which uses a cellular phone and wireless communication to improve the safety of pedestrians. One of the effectual measures against pedestrian-to-vehicle accidents is to make each of pedestrians and drivers find the others and recognize the risk from out of sight and with time to spare for avoidance of accidents. A pedestrian-to-vehicle communication system was developed by using a cellular phone and a car navigation system equipped with GPS and wireless communication function. We focused on intersections as a traffic scene to be covered by the system. After data was exchanged via FOMA in a wide area, information could be exchanged between a pedestrian and a vehicle via WLAN 20 m, 100 m away from an intersection to different directions in about 20 ms. And, the system could give an alarm to pedestrians and cars with collision risk.
7 . GPS-Based Path Following Control for a Car-Like Wheeled Mobile Robot With Skidding and Slipping
YEAR OF PUBLISHING : 2008
Most wheeled mobile robot (WMR) controllers have been developed based on nonskidding and nonslipping assumptions. Unfortunately, wheel skidding and slipping are inevitable due to wheel tire-deformation; consequently, the stability and performance of these controllers are not guaranteed. This brief aims to develop a global positioning system (GPS)-based path following a controller for a car-like wheeled mobile robot in the presence of wheel skidding and slipping. The proposed control scheme uses real-time kinematic (RTK)-GPS and other aiding sensors to measure the WMR's posture, velocities, and perturbations due to wheel skidding and slipping. These measurements are applied to compensate the path following errors based on a backstepping controller. The reported experimental results validate the control scheme. With this solution, the WMR is able to maneuver with better precision in outdoor environments in the presence of wheel skidding and slipping. 2008
8. The design and implementation of an autonomous campus patrol robot
YEAR OF PUBLISHING : 2008
This paper presents the design and implementation of a campus-patrol robot project. Autonomous patrol and web-presence are set as two basic functionalities of the campus-patrol robot. The robot is equipped with diverse sensors. Different data fusion techniques have been applied. An extended Kalman filter (EKF) is used to fuse the data from GPS and electronic compass for the localization and navigation task. And a Bayesian data fusion strategy is used to solve the problem of obstacle detection and avoidance. The web presence of the patrol robot is assured through a website and a web-based remote control platform which allows users to access the real images captured by the patrol robot and to control the viewing angle from a remote place via Internet. Keywords: autonomous patrol robot; multi-sensor data fusion; obstacle avoidance. 2008
9. Remote Sensing & Control of an Irrigation System using A distributed Wireless Sensor Network
YEAR OF PUBLISHING : 2008
Efficient water management is a major concern in many cropping systems in semiarid and arid areas. Distributed in-field sensor-based irrigation systemsoffer a potential solution to support site-specific irrigation management that allows producers to maximize their productivity while saving water. This paper describes details of the design and instrumentation of variable rate irrigation, a wireless sensor network, and software for real-time in-field sensing and control of a site-specific precision linear-move irrigation system. Field conditions were site-specifically monitored by six in-field sensor stations distributed across the field based on a soil property map, and periodically sampled and wirelessly transmitted to a base station. An irrigation machine was converted to be electronically controlled by a programming logic controller that updates georeferenced location of sprinklers from a differential Global Positioning System (GPS) and wirelessly communicates with a computer at the base station. Communication signals from the sensor network and irrigation controller to the base station were successfully interfaced using low-cost Bluetooth wireless radio communication. Graphic user interface-based software developed in this paper offered stable remote access to field conditions and real-time control and monitoring of the variable-rate irrigation controller. 2008
10. Pinpointing the Place of Origin of a Cellular Phone Emergency Call Using Active RFID Tags
YEAR OF PUBLISHING : 2008
When police, fire or ambulance personnel receive an emergency call, they must pinpoint its place of origin in order to respond quickly. When such a call is made from a cellular phone, its place of origin can be determined by using GPS or a cell-based positioning method. However, these methods are sometimes inaccurate and have blind spots. We developed a system for determining location using RFID-reader- equipped cellular phones and RFID tags. We outline the prototype system here. 2008
11. Autonomous Traveling Control of the "TAO Aicle" Intelligent Wheelchair
YEAR OF PUBLISHING : 2006
This paper reports on the development of the "TAO Aide", an intelligent wheelchair with autonomous traveling capability. The wheelchair can accurately determine its position and direction using internal sensors and external assistance from the surrounding environment, including the Global Positioning System (GPS) and radio frequency identification (RFID). It can also detect obstacles it encounters on the road using a laser range sensor. To confirm the effectiveness of our research results, for six months at the Aichi Expo 2005 we demonstrated the wheelchair system by offering trial rides to visitors. This paper describes the total system of "TAO Aide", the positioning method using GPS and RFID, and the autonomous traveling control based on accurate estimations of position and direction using Kalman filtering. Our experimental results at the Aichi Expo demonstrated that accurate trajectory following performance can be achieved using assistance from the infrastructure (GPS, RFID) and that "TAO Aide" could perform safe autonomous traveling without severe accidents 2006
12. Monitoring and Transmission of Heavy Vehicles Parameters using Fixed Cellular Terminal
YEAR OF PUBLISHING : 2006
At present any consignment carried by a vehicle has to travel incommunicado till it reaches the destination. So, both the fleet owner and the persons sending or procuring the consignment have to sit keeping their fingers crossed till the fleet arrives. To track the path of the vehicle and to monitor the various parameters like fuel consumption, kilometers covered and the amount of load in the vehicle an intelligent device would come handy to solve the problem for the fleet operators and the clients. This paper aims at designing an intelligent device, which has two parts: the transmitter and the receiver. The transmitter is set up in the truck and it consists of a microcontroller to which the GPS and the GSM modem are connected. The analog signals from the transducers, which are used to detect the amount of load and the fuel in the truck, are sent to the microcontroller. The microcontroller acquires the position of the truck from the GPS and sends it to the receiver along with the analog values, through the GSM modem using SMS. The receiver consists of a computer to which a GSM modem is connected by its serial port. The SMS is received by the GSM modem and is sent to the computer, which makes use of a map plotting software to plot the position of the truck along with its parameters. 2006
1.Efficient Cost-Based Tracking of Scheduled Vehicle Journeys
YEAR OF PUBLISHING : 2008
Applications in areas such as logistics, cargo delivery, and collective transport involve the management of fleets of vehicles that are expected to travel along known routes according to schedules. There is a fundamental need by the infrastructure surrounding the vehicles to know the actual status of the vehicles. Since the vehicles deviate from their schedules due to road construction, accidents, and other unexpected conditions, it is necessary for the vehicles to communicate with the infrastructure. Frequent updates introduce high communication costs, and server-side updates easily become a bottleneck. This paper presents techniques that enable the tracking of vehicle positions and arrival times at scheduled stops with little communication, while still offering the desired accuracy to the infrastructure of the status of the vehicles. Experimental results with real GPS data from buses show that the proposed techniques are capable of reducing the number of updates significantly compared to a state-of-the art approach where vehicles issue updates at pre-defined positions along their routes. 2008
2. Software/hardware co-design of a vehicle trajectory monitoring system
YEAR OF PUBLISHING : 2008
Using a GPS to navigate, a guard locates a car theft and utilizes vehicle tracking that is, at present, widely employed. In this paper the terminal device using a microcontroller combines a GPS and a GSM/GPRS to make a portable and remote controlling device, and an embedded server is used as a transfer location server. In this way one accomplishes real-time vehicle trajectory monitoring. Clients can remotely monitor a vehiclepsilas position anywhere. Besides, as we have designed the remote monitoring using a virtual comport to combine the existing commercial or free electronic map directly, we need not develop or revise the electronic map software. 2008
3. Intelligent Fleet Management System with Concurrent GPS & GSM
YEAR OF PUBLISHING : 2008
Real-Time Positioning Technology Fleet management system is a rapid growing industry. This system helps institutions to manage vehicle fleet efficiently and effectively through smart allocation of resources. In this project, an intelligent fleet management system which incorporates the power of concurrent Global Positioning System (GPS) and Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) real-time positioning, front-end intelligent and web-based management software is proposed. In contrast to systems which depend solely on GPS positioning, the proposed system provides higher positioning accuracy and is capable to track the target at areas where GPS signals are weak or unavailable. The terminal is powered by Front-End Intelligent Technology (FEI), a comprehensive embedded technology that is equipped with necessary artificial intelligence to mimic human intelligence in decision-making for quicker response, better accuracy and less dependence on a backend server. With less dependency on the backend, large scale fleet management system can be implemented more effectively. The proposed system is successfully implemented and evaluated on twenty vehicles including buses and cars in Universiti Teknologi Malaysia (UTM). Results from the test-bed shown that user can monitor and track the real-time physical location and conditions of their vehicles via Internet or Short Message Service (SMS). The web-based fleet management software also helped the user to manage fleets more effectively. 2008
4. The Design of Vehicle emergent calling system based on gprs
YEAR OF PUBLISHING : 2008
Combining with the working principle of Intelligent Transport System, and with the purpose of enhancing the security of modern traffic, this paper brings forward a project of building a kind of automobile emergent calling system which starts-up with the starting of airbag, the wireless date transport modem, which is droved by serial interface, transmitted the acquired data to the remote monitoring center. The design of the hardware circuit implement, the design of software and the design of building monitor and control center are demonstrated. And finally, the key technique of the system is also discussed. 2008
5. GPS Based Mobile Tele Monitoring and Management System for Inter cities Public Transportations
YEAR OF PUBLISHING : 2008
This paper presents a Tele-monitoring and management system for inter-cities transportation vehicles such as taxis and buses. The system is based on a stand-alone single-board embedded system that is equipped with GPS and GSM modems that is installed in the vehicle. A personal computer based GSM-Server is installed at transportation's head-quarter. While the vehicle is on the move, its real-time parameters such as speed, location, estimated arrival time, road condition and surrounding weather status are reported as SMS message to the transportation's head-quarter GSM-Server for further process. A software package is developed and installed in GSM-server to read, process, analyze and store the incoming SMS messages. Graphical User Interface (GUI) and software management package are developed using Active Server Pages (ASP) and HTML to monitor the fleet and to build profile for each vehicle and driver. The system utilizes the readily available GSM mobile public networks; therefore the fleet administration should not worry about upgrading or maintaining such network. 2008
6.Development of pedestrian-to-vehicle communication system prototype for pedestrian safety using both wide-area and direct communication
YEAR OF PUBLISHING : 2008
We propose a prototype pedestrian-to-vehicle communication system which uses a cellular phone and wireless communication to improve the safety of pedestrians. One of the effectual measures against pedestrian-to-vehicle accidents is to make each of pedestrians and drivers find the others and recognize the risk from out of sight and with time to spare for avoidance of accidents. A pedestrian-to-vehicle communication system was developed by using a cellular phone and a car navigation system equipped with GPS and wireless communication function. We focused on intersections as a traffic scene to be covered by the system. After data was exchanged via FOMA in a wide area, information could be exchanged between a pedestrian and a vehicle via WLAN 20 m, 100 m away from an intersection to different directions in about 20 ms. And, the system could give an alarm to pedestrians and cars with collision risk.
7 . GPS-Based Path Following Control for a Car-Like Wheeled Mobile Robot With Skidding and Slipping
YEAR OF PUBLISHING : 2008
Most wheeled mobile robot (WMR) controllers have been developed based on nonskidding and nonslipping assumptions. Unfortunately, wheel skidding and slipping are inevitable due to wheel tire-deformation; consequently, the stability and performance of these controllers are not guaranteed. This brief aims to develop a global positioning system (GPS)-based path following a controller for a car-like wheeled mobile robot in the presence of wheel skidding and slipping. The proposed control scheme uses real-time kinematic (RTK)-GPS and other aiding sensors to measure the WMR's posture, velocities, and perturbations due to wheel skidding and slipping. These measurements are applied to compensate the path following errors based on a backstepping controller. The reported experimental results validate the control scheme. With this solution, the WMR is able to maneuver with better precision in outdoor environments in the presence of wheel skidding and slipping. 2008
8. The design and implementation of an autonomous campus patrol robot
YEAR OF PUBLISHING : 2008
This paper presents the design and implementation of a campus-patrol robot project. Autonomous patrol and web-presence are set as two basic functionalities of the campus-patrol robot. The robot is equipped with diverse sensors. Different data fusion techniques have been applied. An extended Kalman filter (EKF) is used to fuse the data from GPS and electronic compass for the localization and navigation task. And a Bayesian data fusion strategy is used to solve the problem of obstacle detection and avoidance. The web presence of the patrol robot is assured through a website and a web-based remote control platform which allows users to access the real images captured by the patrol robot and to control the viewing angle from a remote place via Internet. Keywords: autonomous patrol robot; multi-sensor data fusion; obstacle avoidance. 2008
9. Remote Sensing & Control of an Irrigation System using A distributed Wireless Sensor Network
YEAR OF PUBLISHING : 2008
Efficient water management is a major concern in many cropping systems in semiarid and arid areas. Distributed in-field sensor-based irrigation systemsoffer a potential solution to support site-specific irrigation management that allows producers to maximize their productivity while saving water. This paper describes details of the design and instrumentation of variable rate irrigation, a wireless sensor network, and software for real-time in-field sensing and control of a site-specific precision linear-move irrigation system. Field conditions were site-specifically monitored by six in-field sensor stations distributed across the field based on a soil property map, and periodically sampled and wirelessly transmitted to a base station. An irrigation machine was converted to be electronically controlled by a programming logic controller that updates georeferenced location of sprinklers from a differential Global Positioning System (GPS) and wirelessly communicates with a computer at the base station. Communication signals from the sensor network and irrigation controller to the base station were successfully interfaced using low-cost Bluetooth wireless radio communication. Graphic user interface-based software developed in this paper offered stable remote access to field conditions and real-time control and monitoring of the variable-rate irrigation controller. 2008
10. Pinpointing the Place of Origin of a Cellular Phone Emergency Call Using Active RFID Tags
YEAR OF PUBLISHING : 2008
When police, fire or ambulance personnel receive an emergency call, they must pinpoint its place of origin in order to respond quickly. When such a call is made from a cellular phone, its place of origin can be determined by using GPS or a cell-based positioning method. However, these methods are sometimes inaccurate and have blind spots. We developed a system for determining location using RFID-reader- equipped cellular phones and RFID tags. We outline the prototype system here. 2008
11. Autonomous Traveling Control of the "TAO Aicle" Intelligent Wheelchair
YEAR OF PUBLISHING : 2006
This paper reports on the development of the "TAO Aide", an intelligent wheelchair with autonomous traveling capability. The wheelchair can accurately determine its position and direction using internal sensors and external assistance from the surrounding environment, including the Global Positioning System (GPS) and radio frequency identification (RFID). It can also detect obstacles it encounters on the road using a laser range sensor. To confirm the effectiveness of our research results, for six months at the Aichi Expo 2005 we demonstrated the wheelchair system by offering trial rides to visitors. This paper describes the total system of "TAO Aide", the positioning method using GPS and RFID, and the autonomous traveling control based on accurate estimations of position and direction using Kalman filtering. Our experimental results at the Aichi Expo demonstrated that accurate trajectory following performance can be achieved using assistance from the infrastructure (GPS, RFID) and that "TAO Aide" could perform safe autonomous traveling without severe accidents 2006
12. Monitoring and Transmission of Heavy Vehicles Parameters using Fixed Cellular Terminal
YEAR OF PUBLISHING : 2006
At present any consignment carried by a vehicle has to travel incommunicado till it reaches the destination. So, both the fleet owner and the persons sending or procuring the consignment have to sit keeping their fingers crossed till the fleet arrives. To track the path of the vehicle and to monitor the various parameters like fuel consumption, kilometers covered and the amount of load in the vehicle an intelligent device would come handy to solve the problem for the fleet operators and the clients. This paper aims at designing an intelligent device, which has two parts: the transmitter and the receiver. The transmitter is set up in the truck and it consists of a microcontroller to which the GPS and the GSM modem are connected. The analog signals from the transducers, which are used to detect the amount of load and the fuel in the truck, are sent to the microcontroller. The microcontroller acquires the position of the truck from the GPS and sends it to the receiver along with the analog values, through the GSM modem using SMS. The receiver consists of a computer to which a GSM modem is connected by its serial port. The SMS is received by the GSM modem and is sent to the computer, which makes use of a map plotting software to plot the position of the truck along with its parameters. 2006